|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Printed Circuit Design Glossary
Any glossary is bound to include mistakes of fact, emphasis, typography and omission. Please tell us about those you notice - you can cut and paste sections to e-mail us your wisdom.
If you click on these initial or other links and they don't work, probably the whole file is not yet loaded. Just wait a while, or until the busy indicator disappears, and try again.
You can use the Browsers Find facility in the usual way to find things if you prefer.
Symbols A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Symbols
- 274X
- Casual names for an extended RS-274D and RS-274X used to define Gerber Photoplot file format.
-
3rd Angle projection - Representation of a 3 dimensional object by means of
three orthogonal views from the Front, Side &
Top.
See also Isometric Projection.
A
- Designs and parts that use continuously variable
voltage, current, resistance etc. to represent real
world values. e.g. a voltage of 1 Volt might represent
freezing point, and 2 volts boiling point. You
might set switching thresholds for a thermostat using a
comparator.
See also Digital. -
Annotation - Adding notes to a schematic, in particular filling in the legends describing a component (e.g IC2, R45, C3) and labelling the pin tags with the actual pin numbers used in the PCB, allowing for gate allocation, equivalent pin swapping, and similar that may take place during PCB layout.
-
Annular Ring - A Pad Shape consisting of a doughnut shape. Uses
include
- A drill centre mark.
- On a Powerplane, to provide isolation for a drilled hole through it's centre. Plotting for powerplanes is performed as a NEGATIVE - draw where you do NOT want copper. Thus the ring generates an isolated island. The inner section must provide normal electrical clearance plus the tolerance on drill position and layer registration. Many manufacturers prefer an annular ring to an isolating disk because it prevents a void at the drilled hole which might introduce through-plating difficulties.
- Antenna
- A structure to transmit or receive electromagnetic
radiation. In PCB design tracks may be deliberately
designed in lines, loops or spirals to provide such
function (e.g. Key-fob transmitters). They may also
be created unintentionally on high speed signals and
generate interference, or on sensitive signals that
makes a circuit sensitive to external electromagnetic
radiation.
See also EMC. -
Application - Software that performs some end-user task.
-
API - Application Programmers Interface - the facilities and controls offered to applications by the operating system and any add-ons. Normally includes Disk file handling, Timer services, Screen (window) painting, Keyword and Mouse sensing, Network access etc.
- Astable
- A circuit element or wiring of gates that keeps
changing states, usually at a regular rate to provide a
'clock' signal.
See also Bistable and Monostable. -
ATE - See Automatic Test Equipment.
-
Automatic Test Equipment - A test jig designed to test and diagnose finished and/or bare PCBs. See also Bed of Nails and Test Point.
-
Automatic Placement - An automatic facility for Placement. You will need to provide fixed positions for connectors, a board outline, and possibly other constraints for height above board, pairing of components such as decoupling capacitors, and the like.
-
Automatic Routing - A program to take a Rats Nest
and alter the connections paths to attain a pattern
without crossing
tracks, going outside the board area, entering disallowed
areas, etc. Where necessary signals will
move from layer to layer by changing sides at introduced
VIAs. Surface mount pads needing to
connect to a powerplane have appropriate stalks and VIAs
introduced.
Many styles of routing exist. Vutrax supports 3 styles- Basic: A router that basically lays in right angled tracks, vertical on one layer and horizontal on another. Can lay in tracks very quickly and neatly, but will not reach 100% completion. Vutrax includes the Basic router 'Autotrack' which can perform Bus Routing - a great time saver - Track Necking, and various other explicit activities not present in more advanced routers.
- Rip-up: A more sophisticated router including the capabilities of Basic routing, but which can remove and reroute signals to accommodate subsequent signals that can not be routed, and can lay track paths in very complex and imaginative ways when required. These routers can often attain 100% completion. Vutrax includes the Rip-up Router Vuroute.
- Shape-Based & Other Schemes: Advanced routers (with price and system demands to match) that will reach 100% completion if the layout reasonably allows it. These routers are often provided as third party products accessed through Interface Modules.
B
- Carrying back onto a schematic the component legend and
pin numbers assigned during Rats-nest
generation. e.g. naming resistors R1, R2, naming
Integrated Circuits IC1, IC2, with sections of
multi-function packages designated IC3a, IC3b, and showing
the appropriate pin numbers according
to the assigned pin group and the packaging style
(through hole, Surface Mount, Leadless Chip carrier
etc.) selected.
See also Backward Modification.
- In card racking systems, a PCB populated
with rows of connectors to mate with plugged in cards.
Backplanes can provide only interconnections, just a few
termination components, or be active parts
of the systems with bus drivers and possible bus
arbitration facilities.
- Backward Modification
- Carrying back onto a schematic the component legend and
pin numbers assigned during Rats-nest
generation, and subsequently modified during routing. Can
include notifying major changes, but its
most useful function will be updating the schematic to
reflect Pin Swapping, Group Swapping. and
Renumber changes.
See also Back Annotate and Forward Modification. -
Basic Autorouting - See Automatic Routing.
-
Ball Grid Array - A family of square outline configurations with
relatively coarse contact spacing (1.5mm, 1.27mm,
1.0mm, 0.8mm, 0.75mm and 0.5mm). Ball Grid Arrays have
solder balls arranged in four patterns:
Full Grid, Perimeter, Staggered and Thermal Pads. Some
full-grid BGA's have the corner balls missing
for structural integrity.
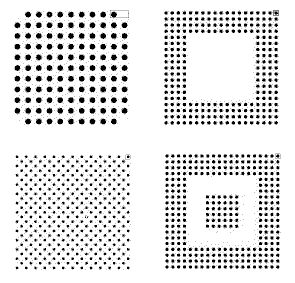
See also Pin Grid Array. -
Bandolier - Components mounted in a double sided strip (resembling a miniature tightly spaced rope ladder) primarily intended for feeding Pick and Place machines.
-
Bed of Nails - A test jig reminiscent of a Fakir's bed of nails. that contacts many points on a PCB to provide Automatic Test Equipment machines access to internal nodes of a PCB. See also Test Point.
-
Bill of Materials - A schedule of the parts needed for a manufacturing.
-
Bidirectional - A pin of the component that can both drive and sense
the connected signal. The decisions to drive or
sense the signal may be made by internal logic (e.g. a
microprocessors data bus pins) or be instructed
by an externally applied signal.
Typically used in Busses. -
Binary - A system using two states - in electronics usually
known as 0 and 1, Low or High (usually voltage),
Negative or Positive (can be voltage or current), FALSE
or TRUE.
The relationships between these depends on the design of the logic system in use, or for gates may be considered to be non-standard to order to obtain different logical functions. e.g. the RS232 modem interface has control signals Positive voltage = TRUE, but for the data signals Positive voltage = FALSE. -
Bistable - A circuit element that has two stable states, and
which the transient application of one or other signals
can be made to change state. A bistable often has two
outputs - the complement (opposite) of one
another, Reset (set to 0) and Preset (set to 1)
signals, and means of changing state - typically a JK
type where the state of two inputs determines what
happens during a clock cycle, and Edge
triggered where the state of one input becomes the new
output state at the rising or falling edge of the
clock signal.
See also Metastable and Monostable -
Bit Image - An image built from Pixels. In the
computer industry such images are used for icons,
diagrams and
photographic images.
See also Vector Image. -
Bitmap - A disk file or memory structure representing a Bitmap
-
Blind VIA - See VIA, Blind.
-
Board Profiling - Cutting a PCB board to the required shape, include inclusion of internal cutouts. Typically performed using a Milling machine.
-
Boolean Logic - The algebraic description of Binary logic. Simple applications include manipulating logical requirements to use different forms of logic for speed or to use available gates.
-
Broken Ring - A Pad Shape consisting of a doughnut shape with cuts
taken out of the ring. It's purposes is to provide
a Powerplane connection to a drilled
hole through it's centre. Plotting for powerplanes is
performed
as a NEGATIVE - draw where you do NOT want copper.
Thus the ring generates an island with
narrow conducting channels through the ring. The purpose
is to prevent heat conducting away from the
drilled pads during soldering because of good thermal
contact with the large copper mass of the
powerplane. Some manufacturers don't want this in which
case these is no pad at such a connection.
Also known as a Thermal Break. See also Annular Ring -
Browser - Most usually applied to application programs that display text, graphics and active links prepared in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML).
-
Buried VIA - See VIA, Buried.
-
Busses - Single signals that visit many circuit elements, often in a very regular pattern. e.g. Microprocessor address and data signals. See also Bidirectional.
-
Bus Routing - Recognising repeating patterns such as occur with rows
of memory IC's and routing with a 'wavy'
pattern that permits high density.
See Automatic Routing.
C
- Short for Computer Aided (or Assisted) Design
-
Caret - Formally a printers mark showing where something is to
be inserted.
Often used in Microsoft Windows systems for a character Cursor. -
Capacitance, Track - Most usually the electrical capacitance between two signals, or a signal and a powerplane, but also 'self-capacitance'. Effects rise time, delay time, EMC emission and Susceptibility.
-
Capacitor - A device providing electrical capacitance. They are measured in Farads, but typical components have values measured in Pico-Farads (10-12F) and Micro-Farads (10-6F). Depending on type they can be polarised, (requiring particular polarity with one end more positive than the other) or not. Typically used to filter out high frequencies, hum and noise (parallel configurations), pass high frequencies with DC isolation (in series with a signal) and form tuned circuits with Inductors.
-
Capacitor, Comb - A Capacitor constructed of PCB tracks by using two comb shapes facing
each other and interleaving
their teeth without touching.
-
Capillary Pens - A liquid ink pen with a metal tip and a fine capillary (and usually a wire) down the centre to carry ink to the tip. Used by draughtsman, and for Pen Plotting where high density and accurately determinable drawn width are required. Only trouble free in very expensive plotters with effective capping of pens and pressure fed ink reservoir.
-
CEM1 - American name for SRBP , material used as a Substrate for a PCB..
-
Centre Line - A special form of Dash Line consisting of alternative 'dot' and 'dash' drawn sections.
-
Clearance Rules - The required clearances between conducting traces on the
PCB (including signals, power rails,
mounting holes etc.).
A simple rule for a simple low voltage PCB might be 0.008" (8 THOU) clearance between all items.
Circuits involving high voltages will require substantially higher clearances, and safety standard may impose very large clearances (say 0.1" (100 THOU) between mains voltage traces and low voltage (safe) side signals. Some processing may include different clearances on different layers, between tracks or tracks and pads, and between different classes of signals. -
Corner - In Vutrax, any position where a track changes direction or width - a Vutrax ANGLE point.
-
Coordinate - A position relative to an origin, expressed in Vutrax as X and Y values relative to some arbitrary 0, 0 position. They may be expressed in Imperial or Metric values. For Vutrax the coordinates can take either sign - Positive X is to the right, Positive Y is downwards.
-
CMOS - Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. This technology, and its many developments, offer extremely low current consumption in quiescent (i.e. unchanging) states, and has become a primary technology in the design of Integrated circuits for digital circuitry.
-
CNC - Short for Computer Numerical Control
-
Comb Capacitor - See Capacitor, Comb
-
Computer Numerical Control - Normally abbreviated to CNC. The definition of
drilling and milling (also known is routing - not to be
confused with the differently pronounced finding routes
for signals) for a PCB.
Drill data has a well established format known as Excellon. -
Component - A physical part to be mounted on a PCB. Examples include an Integrated Circuit (IC), Discrete Transistor, Resistor, Capacitor, Inductor, Transformer, Connector assembly, Fuse holder.
-
Component, Height - The height above board level that a component requires. In designs where a card is fitted into a case the maximum height may vary over the area of the board. Thus component height becomes a critical factor during Placement.
-
Conductance, Track - The reciprocal of Track Resistance
-
Conductor - Something that carries electricity with very little resistance. e.g. A Copper track on a PCB
-
Connector Fingers - Metallic pads at the edge of a PCB, sometimes on a
specially shaped profile, that plug into an external
socket. e.g. a IBM PC ISA bus.
Such fingers are usually plated, often with gold. To accomplish this it is necessary to provide a Plating Bar -
Connectors - Normally a component mounted on a PCB that is used to
provide electrical connection with external
equipment.
Exceptions: Connector Fingers are connectors forming part of the PCB. Sometimes critical signals (e.g. very high frequency) are connect by a cable from one place on a PCB to another.
A huge variety of connectors are used on PCBs, which include- Direct - e.g. Fingers used in the ISA bus
- Indirect - e.g. Soldered on connectors used in PCI bus.
- Header Plugs - Rows of pins accepting IDC sockets.
- Screw Clamps - either screwing onto a PCB copper area, or a component with grub screws, generally used where substantial current capacity is required.
- Special - Telephone connectors, Video Connectors, etc. mounted so that they are accessible through holes in the casing.
-
Connection List - The interconnections for a circuit expressed as which
of each pin of each device is connected to other
pins.
Typically takes the form of a Pin-to-Pin List or a Device Oriented List -
Copper - Metallic Element, Symbol Cu, atomic No. 29, atomic
weight 65.54, Specific Gravity 8.92 @ 20C,
Resistivity 1.68E-8 (0.0000000168)
Ohm Metres @ 20C
By far the dominant material used for PCB Conductor tracks, having one of the lowest resistances of suitable metals.
Reacts slowly with oxygen in air and hence tarnishes, requiring cleaning procedures prior to soldering, and usually protection (resists) to metal that would be exposed in the finished product. -
Copper Fill - Filling an area of a PCB not directly need for carrying signal (i.e. the bare Substrate) with a solid area, Hatching or Crosshatching. This can provide for control of electrical noise (Susceptibility and emission), to provide a Heat Sink, or to provide similar copper density over the whole PCB for processing and/or warpage considerations.
-
Copper Pour - Non-Vutrax proprietary name for Copper Fill.
-
Copper Sharing - Using a single section of track to carry a signal to more to more than one pin. A common space saving tactic, but can not be used with some logic systems such as ECL which mandate a single signal path, or where tight control of signal time and Track Impedance is required.
-
Crosshatch - Filling an area with two sets of parallel lines at an
angle to one another. Normally lines at 45 degrees
either side of vertical are chosen.
See also Copper Fill. -
Cursor - A 'you-are-here' indicator. Some of the forms it can
take :-
- A marker showing where the next character typed will appear. May be an underline symbol, vertical bar, or flashing character cell. See also Caret.
- A Crosshair, centre 'target' or other exact position indicator used to locate position in graphics programs.
-
Current Capacity - How much current can be carried by a wire, PCB track,
or other Conductor. Normally limited
by
safe and/or reliable rise in temperature.
The Bookcase section of the Vutrax web site includes a detailed section of current capacity of PCB tracks. -
Curve - A non-straight line. In the Vutrax context a curve is stored in its segmented form built of 'Curve' point.
D
- A line draw with alternating drawn and space sections. The drawn and gap sections can take many sizes according to context, to provide construction lines, 'fold' lines, alignment indicators etc. Particular forms include alternating dot/dash for Centre Lines, finely dotted construction lines, short dashes for hidden edges, and pairs of dashes for ditto.
-
Decode, Gerber - Reading a Gerber Photoplot file and decoding it to produce a PCB artwork file in the PCB design system format.
-
Decode, Emma - Reading an Emma Photoplot file and decoding it to produce a PCB artwork file in the PCB design system format.
-
Design Checking, Dimensional - Checking signals on a PCB design for:-
- Required clearance between signals. This may vary from simple 'single clearance' for all signals, to complex arrangements with different clearances between different signals, between different items (e.g. pads, vias, tracks), and different clearances on inner/outer layers.
- Organisation of pad stacks, Blind and Buried Vias, to check for correct connectivity and isolation.
-
Design Checking, Interconnect - Comparison of a PCB with its original interconnect requirement.
-
Design Checking, Logical - Various design checks including:-
- Signals are fully connected on allowable layers with necessary minimum width.
- Pads and VIAs meet some minimum size criteria.
- Surface Mount pads connect to VIAs used for connection to powerplanes (where relevant).
-
Design Checking, Classes - A scheme for classifying signals in classes - e.g. Digital, Analogue, Mains supply, Low voltage power. These classifications can be used to define requirements for clearance between such elements of the design for safety and functional purposes.
-
Design Rules - The definition of design requirements in terms of signal isolation, minimum width, layers used, and a many other more specialised checks.
-
Device - A single physical component (e.g. an IC, Resistor, Coil) or an assemblage Treated as a single element (e.g. a Hybrid, Power supply module).
-
Device Oriented List - Lists the connections in a circuit by listing each
device pin and naming the signal to which it is
connected
74LS00 A CLOCK A ENABLE Y LATCH\ - Digital
- Designs and parts that represent exact values (usually
0 and 1, or FALSE and TRUE.). The type of
electronics is also often know as Logic Circuits.
See also Analogue.
Note that even digital circuits represent their 'digital' values as analogues - e.g. a logic system might sense 0 as a voltage less than 0.8V, and 1 as more than 1.8V. Drivers would normally guarantee a voltage less than 0.4V or more than 2.4V to provide reliability. Voltages between 0.8V and 1.8V would be 'undefined' and must occur only during state changes if logic is to be reliable. -
DIL or DIP - See Dual In-Line Packaging.
-
Diode - A component conducting current in one direction only,
used for rectifying AC to DC, as part of RF
detectors, catch diodes across actuating coils, and many
other purposes.
Various specialist versions include so called Zener diodes which break down at a specified reverse voltage, and can be used for voltage regulation, Shottky Diode with very high speed characteristics, LED and many more. -
Dimension - To annotate a drawing or PCB with sizes, distances between critical positions (e.g. mounting holes), radii of profiling, drilled hole sizes, etc.
-
Directory - A disk file, or the bottom level of a disk drive, that contains the names, dates, sizes, and filing system references to files and/or further directories. In Microsoft operating systems often called a Folder.
-
Disconnect - In Vutrax, removing a point to point track connection, usually to insert an alternative connection elsewhere.
-
DOS - Disk Operating System.
In modern usage normally applies to the text based operating system first using on Personal Computers from IBM (PCDOS) and Microsoft (MSDOS). Emulations of this operating system can be found in Windows. -
Double Sided - A circuit board with tracks on both sides. Typically
one side of the PCB is used for vertical tracks,
and the other side for Horizontal. VIA
holes are used to carry signals from one side to the
other.
See also Single Sided. and Multilayer -
Drilled Size - The size of the drill used to make a hole in a PCB. For plated through processing, this will be larger that the Finished Size to allow for the build up of metal during plating.
-
Dual in Line - Style of IC packaging when the package includes two rows of pin-through pins. Pin spacing in each row is 0.1" (100 THOU). Rows spacing is 0.3" for small devices, 0.6" for large (e.g. 24 pins upwards) but some variants exists.
-
Dumbbell Pad Shape - A pad shaped consisting of two circular ends joined by a narrower waist. (Not a 'native' shape for Vutrax - if you need these draw them as a Trace Pad.)
-
Duroid - A material used as a Substrate for a PCB in high frequency designs. .
-
DXF - Data Exchange Format originated for import and export of drawings for AutoCAD. Adopted by many CAD packages as a convenient means of transporting drawing data. Does not provide many of the features required for advanced PCB design.
E
- Connections on a PCB and/or external cabling that
provides multiple routes for earth current.
Oscillating magnetic field passing through the 'loop' will
induce potential differences in the earth system.
A typical cause of 'hum' in audio systems, and related
problem in video and Digital systems.
See also Earth Star. -
Earth Star - A single point to which earth connections are made, either to avoid Earth Loops or to provide a single connection between multiple earthing systems within a PCB (e.g. Analogue earth, Digital and Mains earths may all be connected at a single point).
-
ECL - Emitter Coupled Logic - a style of extremely high speed logic (now superceded for most applications). The signals for ECL are normally constrained to be a single long trace starting at the driving pin, through input pins, and finally terminating resistors.
-
EIDE - An extended form of IDE to support addressing of larger disc drives.
-
Electromagnetic Compatibility - The requirements for electronics products to neither interfere with other equipment, nor to be effected by prescribed level of Electromagnetic Radiation themselves. Normally abbreviated to EMC.
-
E-mail - Electronic Mail - The ability to send messages, and often file attachments, to other users of a Network. Most usually, sending messages to other users of the Internet.
-
EMC - See Electromagnetic Compatibility.
-
Ethernet - A LAN technology offering connection
based on IEEE802.3. Forms include
- Standard Ethernet - a single length of thick coaxial cable with transceivers operating at 10M Bits/sec.
- Thin Ethernet (10Base2) - based on Thin cable and BNC connectors, with lower length and connection capability than Standard Ethernet, much simpler to install, and running at 10M Bits/sec. Machines are daisy chained through 'T' connectors.
- Twisted pair (10Base-T) - based on a 'hub' scheme using RJ-45 connectors. The topology provides greater resiliency than single cable or daisy chained schemes.
- 100M Bits/sec versions are becoming available.
-
Emma Photoplot - A proprietary form of Photoplot commands used by Quest photoplotters. Now relatively uncommon.
-
Excellon - The de-facto standard for Computer Numerical
Control CNC data for PCB drilling data originated
for use with Excellon drilling equipment.
There are many variants to this format, including different basic units, precision, suppression of leading or trailing zeroes, suppression of duplicate coordinate values.
F
- See Transistor, FET.
-
Fibreglass - A common material for the Substrate of a PCB. A particular advantage of this material is that it's thermal expansion characteristics are close to those of copper tracks. See also FR4.
-
Fiducal - Small copper land (diamond, circular or square) approximately 1.6mm diameter, with large resist opening, used for locating marker for pick and place equipment Usually defined as a Node in Vutrax..
-
Fillet - Applying a radius to an otherwise sharply angled edge. Sometimes use on PCB tracks to remove discontinuities that might create electrical reflections, and where a Mitre is insufficient.
-
Fill, Solid - Filling an area with an unbroken surface of copper. See Copper Fill.
-
Fill, Coarse - A Vutrax pre-selected solid fill style that does not try to follow fine detail. See Copper Fill.
-
Fine Pitch - General term for a PCB design where standard spacings of pads, tracks etc. is close to manufacturing limits.
-
Finger Pad - One of a row of pads used for Connector Fingers.
-
Finished Size - The size a hole through a PCB after it has been plated through. See also Drilled Size. Many PCB designers specify only the Finished Size and allow the manufacturer to make allowance for plating thickness according to the process used.
-
Firmware - The basic program of a computer or peripheral device
stored in some sort of 'permanent' memory.
e.g. a PC BIOS, CD-ROM drive manager.
Modern firmware is often stored in updatable 'flash' memory, rather than requiring chip exchange. -
Firewall - A protected interface between an external Network (usually the Internet) and a local private computer or network (often an Intranet).
-
Flat Pack - A component packaging style used in some military designs.
-
Flexible Circuits - Designs on a flexible Substrate that allows the circuitry to be bent to fix a particular enclosure and or provide displays and control on different planes without the need for connectors to separate rigid boards.
-
Flip - In the PCB CAD context:-
- To move a component onto the opposite side of the PCB (requiring a layer change and mirror-image).
- To view the PCB as if from the back side.
-
Flip-Flop - See Bistable.
-
Folder - A disk file, or the bottom level of a disk drive, that contains the names, dates, sizes, and filing system references to files and/or further folders. Also commonly called a Directory.
-
Footprint - The physical layout required for a PCB mounted component, including its pads, physical outline, and any allowance for chuck sizes of pick-and-place machines or necessary heat sinks or mounting hardware.
-
Footprint Library - A ready built, or user built, selection of Component Footprints.
-
Font - A Character or symbol Typeface.
Great care must be taken in using general purpose fonts in PCB designs because photoplotting machine may use 'similar' fonts that cause electrical shorts or printed text filling holes with ink. Vutrax avoids these problems by evaluating fonts in the design file, or using it's own strictly defined fonts. -
Font, True Type - A Character or symbol Typeface (typically available in Microsoft Windows) designed to be easily and attractively scaled to a range of sizes. See also Font.
-
Forward Modification - Processing changes made to a schematic or Netlist, and
applying them to a fully or partially routed
PCB design, attempting to alter as little of the
existing design as feasible.
See also Backward Modification. -
FR4 - A material used as a Substrate for a PCB, made of fibreglass & epoxy. Cheap, and reliable except where exposed to moisture, this is the most commonly used material for double sided and multi-layer boards..
-
G
- General term for a simple logic element such as an AND, OR element
-
Gate Swapping - Exchanging whole functional groups of pins in multi-gate
packages, or between similar packages, to
make routing easier (e.g. reduce signal length or number
of signals crossing).
See also Pin Swapping and Back Annotate. -
Gate, And - A logic element that produces a TRUE output if and only if all inputs are TRUE.
-
Gate, Nand - A logic element that produces a FALSE output if and only if all inputs are TRUE.
-
Gate, Nor - A logic element that produces a FALSE output if one or more inputs are TRUE.
-
Gate, Or - A logic element that produces a TRUE output if one or more inputs are TRUE.
-
Gate, Xor - A logic element that produce a TRUE output if the two inputs have opposite states. XOR is short for Exclusive Or.
-
GDI - Graphical Device Interface - usually used to refer to the interfaces provides by Microsoft Windows for screen and printer layout definition.
-
Gerber Photoplot - A proprietary form of Photoplot commands used by Gerber photoplotters, and many other makes - the de-facto standard enshrined as RS-274D and an extension RS-274X.
-
Glue Spot - When Surface mount devices are placed on a bare PCB
they must be held in position until soldering
takes place. This is often accomplished by using one or
more spots of specialist glue already placed on
the PCB.
Some manufacturers insist on the spots being placed on top of a copper area, others onto substrate, and some 'don't care'.
The positions of these spots must often be tabulated for use in machines used for placing these glue spots. -
Gold Plating - The process of applying a gold coat to parts of the
PCB used as a connector. A typical use is in
producing Connector Fingers.
See also Plating Bar. -
Grid - Many designs are conveniently based on a grid so that
alignments are easily managed. For a schematic
the grid may be 0.05 inch to match a small multiple of
typical component tag pitch. For PCB
design a
grid might be half the typical pin spacing to easily
facilitate a single track between pads.
-
Ground - The nominal voltage reference, often called GND, 0V or similar. Complex designs may have a number of separate 'Grounds' that are either isolated or joined at an Earth Star
-
Ground Loop - See Earth Loop.
-
Groundplane - See Copper Fill.
-
Group Swapping - Another Vutrax term for Gate Swapping.
H
- The physical items of a computer including the processor, RAM, Disk storage system, Display, etc.
- Parts associated with electronic components such heatsinks, mounting clips, and isolating washers.
-
Hatch - Filling an area with a set of parallel lines, Normal
chosen to be horizontal, vertical or at 45 degrees.
See also Copper Fill. -
Heat Sink- A specially constructed item with large surface area fixed to a component to cool it. May vary from a small piece of metal to a major construction incorporating cooling fans.
- An area of copper on a PCB in thermal contact with a high dissipation device to provide for cooling.
Hertz - The unit for frequency of oscillation.
Measured in, and sometimes still called, Cycles per Second, Symbol Hz. -
Hierarchy - In the Vutrax context, an organisation of schematic drawings where separate drawings reference one another. Typically a block diagram overview references schematic detail for its various subsections, and so on as required.
-
Histogram - A diagram showing some measured quantity measured over
some range of controlling variable as a
series of bars, the bar height or length (depending on
vertical or horizontal orientation) reflecting the
value measured.
Within Vutrax, a histogram of track density can be displayed to assist in Placement. -
HTML - Short for Hypertext Markup Language
-
Hybrid - A tiny circuit built using copper tracks, resistive inks, fabricated inductors and capacitors, and un-packaged components, to build a functional unit often encapsulated in a manner similar to an Integrated Circuit
-
Hypertext Markup Language - General term for Internet standards
for displaying pages of formatted text, graphics and
active
(clickable) elements. Often known as HTML.
See also Browser. -
Hz - Symbol for the unit of frequency Hertz.
I
- IDC
- Short for Insulation Displacement Connector.
-
IDE - Integrated Drive Electronics - basically a disk drive with embedded computer interface electronics - the connection to the computer is basically just a buffered 'AT' IO bus. Often two per motherboard, with up to 2 drives on each. Reliable operation with 2 drives per cable often requires matched drives.
-
Impedance Matching - Arranging that certain signals have similar characteristics regarding resistance, capacitance and inductance. Typically required for related signals (e.g. clock and data) in very high frequency designs.
-
Inductance, Track - Measurement of the way in which the track behaves intentionally or otherwise as a inductor.
-
Inductor - A component providing inductance, typically an air or ferrite cored coil, but small values may also be provided using a Spiral track.
-
Index, Schematic - A Vutrax file SCHEMLIB.LIX built by utility SCHEMLIB that is used for browsing for schematic symbols.
-
Index, Rats Nest - A Vutrax file FOOTLIB.LIX built by utility FOOTLIB that is used during Rats-nest building to find the physical footprint libraries for the devices required.
-
Index, Object - A Vutrax file OBJLIB.LIX built by utility OBJLIB that is used for browsing for general purpose (not schematic) symbols while drawing.
-
Insulation Displacement Connector - A style of connector that connects by forcing the
cable complete with insulation into the connector,
where the insulation is cut through and a gas-tight
connection established between the connector and
the metallic core of the cable.
Although used for individual connections in specialist applications, PCB use is usually for mass-connecting ribbon cable to a connector. -
Integrated Circuit - A component containing many functional elements. Typically manufactured on a single substrate (e.g. Silicon) but may also be a Hybrid
-
Interface Module - In Vutrax, an installable module used to provide such items as Additional Libraries, Interfaces to third party products such as Databases and Routers, or to provide additional processing modules (e.g. Raster to Vector conversion).
-
Internet - The international computer Network
providing the backbone for a series of protocols
providing
E-mail, News, File Transfer, World Wide Web, and other
services
See Browser, Web Site and URL and. Intranet -
Intranet - A private Network providing services similar to that of the Internet but either completely private, or connected to the Internet through a Firewall or other limited access scheme.
-
Isometric Projection - Representation of a 3 dimensional object by means of a
projection where vertical edges are shown
vertically, but the remaining axes lie in parallel
receding lines at 30 degrees above the horizontal.
See also 3rd Angle projection -
Input - A pin on a component that senses a signal but does not attempt to set its level (though probably provides some loading to the signal).
-
Interconnection - The electrical connection between two component pins or other items.
- Invert
- To view the image inverted or upside down (i.e.
reversing the direction of the Vertical (Y) coordinate),
- or to turn a selected item upside down without changing the left and right sides.
J
- A set of just the required Vutrax job-specific library items is extracted into a single file. This file can be stored with the Project so that even if libraries are subsequently altered the original job can be reproduced and modified.
K
- A material used as a Flexible Substrate for a PCB. Difficult to manufacture, and expensive, but valuable for designs that must be folded..
- An area of a PCB, on one, some or all layers, in
which any of routing, VIAs or components may not
appear.
e.g. Areas to be cut-out or near mounting points, or areas under components where pin-through will be required. -
Kitting List - List of parts needed to populate a bare PCB with components.
L
- LAN
- Local Area Network - a typically office wide network using local high speed interconnection technologies such as Ethernet or Token Ring.
- Soldering pad, plated through/SMD component land.
-
Latch - See Bistable
-
Label - In Vutrax, naming a specific connection on a Schematic to a pin where drawing in the connection would be untidy, or where the connection is to a pin on another drawing.
-
Laser Photoplot - Many modern Photoplotters actually
write to the film using laser generated bit image. Most
machines
'emulate' traditional photoplotters in term of 'flashing'
pads and drawn traces of selectable width.
RS-274X was developed as an extension to RS-274D primarily to make optimal and automatic use of the virtually infinite 'apertures' available. -
Laser VIA - See VIA, Laser.
-
Leadless Chip Carrier - A style of IC package where the connections are designed to contact a specially made carrier rather than pin-through or soldered surface mount.
-
LED - Light Emitting Diode
-
Legend - A text label identifying a device.
See also Silk Screen. -
Libraries - A general term for a collection of pre-prepared Vutrax
items such as:-
- Schematic Library - circuit diagram symbols for gates, resistors, connectors etc.
- Object Library - symbols for non electrical items such as cabinets, windows, etc.
- Footprint Library - graphical representation of the pads and silk screen for PCB components.
- Physical Library - a processed form of libraries used for Rats Nest generation often built by associating the schematic symbol with the footprint symbol. Multiple footprints may be tabulated for a device (e.g. DIL and SMSO).
-
Light Emitting Diode - A diode that when carrying current in the forward direction emits light. The light of most such devices is nearly monochromatic, and 'light' includes infra-red often used in beam-break detection. Two coloured LEDs are really two LEDs back to back. Alternation above the rate of persistence of vision can produce the effect of intermediate colours.
-
Linux - A variant of the UNIX operating system, originally designed Intel 'PC' processors (386 to Pentiums) but ported to many other platforms
-
Logic - See Digital.
M
- Casual term for Interactive - doing operations by a series of point and click operations, rather than some automated procedure.
-
Metafile - A memory or disc file containing an image in the form of drawing instructions, rather than as a Bit Image. See also Vector Image.
-
Metastable - An indeterminate state for a logical system. Typically occurs when sample and hold times are not adhered to in devices such as a Bistable and the logic hovers in a transient state for an indeterminate time. One of the causes of random failures in digital systems - any asynchronous external event can not with certainty be sampled without the possibility of a Metastable state.
-
Microstrip - A signal on a PCB, usually carrying high frequencies or with very fast rise time, that is carefully dimensioned and laid over a ground return trace on an adjacent or both adjacent layers, to provide precise control of signal delay, Track Impedance, and end reflections. See also Transmission Line.
-
Microvias - See VIA, Laser.
-
Microwave - Circuitry operating at frequencies where the wavelength is 1mm to 30cm (300GHz to 1GHz) - between radio and infra-red wavelengths. Such frequencies on PCB require extreme attention to exact track form.
-
Mitre - Applying a straight edge cut across an otherwise
sharply angled corner or edge. Quite common on
PCB at right angled track junctions to improve
manufacturability, reduce electrical reflections, and
sometimes for purely cosmetic purpose.
See also Fillet -
Mirror - To reflect the view in a vertical mirror (i.e. reversing the direction of the Horizontal (X) coordinate). See Flip.
-
Modem - Modulator/Demodulator - a device that converts digital data to a form that can be transmitted by a telephone line. Most typically converts the signals to speech band sounds. See also Networks.
-
Monostable - A circuit element that, on application of an external
signal, changes to another state for a selected
period and then reverts to the rest state.
See also Metastable, Bistable and Astable -
Multi Chip Module (MCM) - A module or package capable of supporting several chips in a single package.
-
Multilayer - General term for using more than 2 layers for a PCB.
Multilayer boards usually have an even number of layers because the board is constructed from separately manufactured double sided sheets bonded together.
N
- Numerical Control.
- A common name for No Connection - the name assigned to component pins intentionally left disconnected. Vutrax uses the name N/C.
- Network
- Interconnection of local (LAN) or distributed (WAN) computer systems to allow sharing of resources, provide messaging, etc.
- Net List
- Description of a circuit in terms of a list of which component pins are connected together. May include naming of the signals. See Pin-to-Pin List
-
Noise - Electrical interference from adjacent circuitry or injected into power supplies or the ground by other circuit elements, externally induced, or inherent in the circuit elements. Although most obvious in Analogue circuitry (e.g. hiss in an audio amplifier) noise can cause malfunction in Digital circuitry if its peak level is sufficient to exceed the logical thresholds. See also EMC
-
Numerical Control - Controlling a machine with numeric data (and usually alphabetic or symbols command characters or words) produced by a design system. See also CNC.
O
- The electrical laws determining current flow through a
resistance R (Ohms) with applied voltage
V (Volts) and resultant current I (Amps) and
dissipation (energy generated in the resistance) of
W (Watts).
- I = V / R
- V = I R
- R = V / I
- W = V I = V2 / R = I2 R
-
Operating System - The software on a computer that provides varying
degrees of services (e.g. managing disk filing) and
protection (e.g. log-in, multi-programming).
The current most common are UNIX (including Linux), DOS, and of course Windows. -
Optimise - In Vutrax, re-organising the connections of a signal to meet some criteria - often finding the shortest overall track length.
-
Orthogonal Routing - A style of routing dominated by horizontal and Vertical
tracks on different layers.
See Automatic Routing. -
Origin - Some nominal starting point for a coordinate system. While working, step sizes may use a variable origin based on the last selected position.
-
Output - A pin on a component that consistently drives the signal to a level determined by the component.
P
- A shape of copper used for mounting components, drilling through for a VIA or mounting hole. See Pad Shapes.
-
Pad Shapes - Vutrax support a variety of Pad shapes
including Circular, a circle with a stretched parallel
centre
(Elongated), Axial or 45 degree Rectangular or Square, Broken Ring, Annular Ring, Drill cross,
and Trace Pad - a user
constructed shape.
See also Pad Stack. -
Pad Stack - Pad Shapes. may need to vary in
different circumstances - e.g. on a Solder Resist and/or on top
side, back side or internal layers.
Such variations can be explicitly defined by providing variations tabulated for different circumstances, or left to generalisations such as 'oversize' and 'undersize' by selected amounts. -
Panellise or Panelize - Take a PCB layout, and step and repeat it for
manufacture of a number on a larger sheet.
Similarly, to take a number of separate PCBs and merge them into a single panel (which may also be stepped and repeated) - a common occurrence in domestic equipment when the break lines are clearly visible. -
Parts List - A list of the parts required to build specific quantities of one or more PCB (and often associated equipment).
-
PC- Personal Computer - to be interpreted as an industry standard' architecture desktop computer, or any computer design for personal use according to context.
- Printed Circuit see PCB.
PCB - See Printed Circuit Board.
-
PC Card - A marketing renaming of PCMCIA.
More generally, any interface card that fits inside any Personal Computer. -
PCMCIA - Credit card sized interface cards primarily used in Lap-top computers for adding modems, network connection, CD-ROM drives and the like. See also PC Card.
-
Pen Plotter - A device to output graphics data by drawing on paper
or film using ink based pens. Often a variety of
pens can be selected by the software to provide
multi-coloured output and/or a variety of drawn line
widths to speed up plotting of wide lines or filled
areas.
The most common and trouble free pens have fibre tips, but ball tips and Capillary Pens may also be used. -
Photoplot - Output of graphics data by 'drawing' and 'flashing'
selected shapes into photographic film. Such plots
can be accurate to small fractions of THOU. Undoubtedly
the preferred means of outputting PCB
masks for direct use in manufacturing.
See also Gerber Photoplot, Emma Photoplot and Laser Photoplot. -
Photoplot Viewer - Software for previewing the output to be expected from Photoplot data. Many free viewers exist, often as non-saving issues of more capable editors for finished PCB layouts.
-
Photo Reduction - High quality output of PCB layout at natural size is difficult without the use of a Photoplot. To avoid photoplotting such output can be plotted at (say) double size, and then scaled to the natural size (Photo Reduced) using a large format camera, (and usually a contact print to produce a positive).
-
Physical Library - See Libraries.
-
Pick and Place - Notionally Picking components from stock and Placing them in the appropriate position on a PCB. In practice machines that do this either select between multiple Bandoleers, or are fed the components in correct sequence from a single (or only a few) Bandoleers specially made for the job.
-
Pin Grid Array - A family of square outline configurations with pins
around the edge in a variety of numbers of rows, for
insertion into drilled pads and soldering conventionally
from the back side. Extensively used for
microprocessor parts.
See also Ball Grid Array. -
Pin Swapping - Exchanging signal connections to a device so that
routing is easier (e.g. so that the signals no longer
cross). Generally the pins have equivalent functions (e.g.
the 2 inputs of an AND gate).
See also Gate Swapping and Back Annotate. -
Pin Through Hole - A Pad which includes a hole drilled
right through the board to accommodate a component pin,
or to
be fitted with a pin carrying signals to other layers.
See also Plated Through Hole. -
Pin Through - Connect tracks on either side of a PCB by passing through a pin or wire which is solder, rivetted, or otherwise connected to both sides.
-
Pin-to-Pin List - Lists the connections in a circuit by listing the
device pins that each signal visits. The signals do not
have to be named. e.g.
IC1 5 R4 1 IC6 3 -
Pixel - Short for Picture Element, each 'dot' element of an
image is a pixel.
Each pixel has a luminance, and may have colour attributes. Typically represented as:-- 1 bit: Full On, or Off. Usually, but not always, 0 is dark and 1 is light).
- 4 and 8 bit: Selects from a 16 or 256 bit 'palette' of arbitrary colours.
- 16 bit: A colour system approximating 'full colour'.
- 24 bit: A colour system representing colours by 8 bits each for Red, Green and Blue (All ones = full intensity, so 0,0,0 = Black, 255,255,255 = White, 255,255,0 = Yellow). Often called Full Colour.
- 32 upwards: Systems used in professional digital imaging.
-
Placement - Arranging the components on a PCB to fit the required
board outline, height & thermal limitations, and
external connector positions, such that it is possible to
route the interconnections given the allowable
number of layers.
Alignment of memory IC and other bus based components will be a major factor, as will be providing 'routing channels' for high densities of signal traces, and provision of space around high density parts (e.g. microprocessors). Good initial placement requires many years of layout experience.
You haven't got this experience? Try Automatic Placement for an initial layout (or just guess), run Automatic Routing, until it is obviously making very poor progress, stop the router and see where the layout is deficient from the bulk of unrouted signals. Save the current layout (in case you make things worse) and then try to organise the layout to remove the bottlenecks or provide more room for them. Use the rubber-band signals moving to the 'nearest' connection to try to minimise connection length. Try routing again, and so on until you find a solution (or one that can be manually finished) or decide you need a larger PCB or more layers. -
Placement, Automatic - Component Placement using a program provided with various constraints (e.g. fixed connector positions and Component Height) and attempts to find a workable component layout by aligning components, looking for shortest track length, and various other strategies.
-
Plan and Elevation - See 3rd Angle projection
-
Plated Through Hole - A hole drilled through a PCB that is then internally plated to provide connection between the layers. The most common type of hole on double sided and multilayer PCB's, and is used for conventional component mounting and for VIAs.
-
Platform - The operating environment for software.
For an Operating System this includes the Hardware and Firmware.
For an Application this includes the above plus the Operating System and possibly other interfaces such as a specific Network, databases, and graphical front-ends. -
Plating Bar - Used with designs using Connector Fingers to provide a means of electro-plating the fingers. The bar provides connection to all of the fingers, the connections being machined away during final board profiling.
-
Plotter, Pen - A plotter, often for very large sheets of paper, that
uses one or more pens to draw an image. The pens
are often exchangeable, and of different colours. For
critical dimensioned output the pen may be a
capillary ink type.
Small Pen Plotters have been largely superceded by desktop inkjet and laser printers which are much less temperamental. -
Plotter, Photo - A specialist plotter providing very high accuracy output by drawing with light onto photographic film. Items can be drawn to accuracies of fractions of THOU at 1:1 scale for direct use in PCB production. This is the modern means of choice to produce PCB manufacturing masks.
-
Plug & Play - Equipment and drivers that can tell the operating
system what it is, requires, and what settings are
available, and can then configure itself as the host
system requires.
An operating system that can interrogate peripherals and allocate resources as required (sometimes during startup, sometimes, particularly for PCMCIA cards, on-the-fly). -
Polyimide - A material used as a Substrate for a PCB. Has superior thermal coefficient of expansion over FR4, and rated for higher temperatures. Consequently, often used in military designs. .
-
Postscript - A page description language for defining text, text fonts, and graphics.
-
Power Input - A pin on a component that provides a ground reference or provides a power supply
-
Power Output - A pin on a component that provides power to other components - e.g. the output of a voltage regulator.
-
Power Supply - A unit that provides appropriately regulated power
supply to a PCB or other equipment.
A misnomer - the 'supply' is usually the mains or battery - the Power Supply is really a Power Converter. -
Powerplane - A layer of a multilayer PCB that is used to provide
an earth reference or Power feed. Each connection
to the plane is through a Plated Through Hole.
Holes through the PCB that do not connect to the plane provide isolation at the drill position - see Annular Ring.
Holes through the PCB that do connect to the plane may need to provide a Thermal Break. -
Powerplane, Split - A Powerplane that carries more than one power supply or ground on a single layer. This is only possible if the design is physically partitioned (e.g. into physically separate digital and analogue sections).
-
Printed Circuit Board - A electronic circuit produced using tracks of Copper (or some other suitable Conductor) on a
Substrate.
Manufacture is usually accomplished using variations of the following (with apologies to the guys who do this job!):-- Coating a Substrate with a thin copper coat and a photo-sensitive (usually Ultra-violet (UV) sensitive) film.
- Expose using a transparency of the required pattern (positive or negative depends on process). For double sided board expose both side with accurate registration.
- Develop the coating so only the tracks are coated.
- Etch the board to remove unwanted copper.
- Drill holes where required.
- Plate the copper with more copper (professional processing only - one off designs typically use sufficiently thick copper initially).
- For multilayer boards bond the layer pairs into the final form.
- Plate through the drilled holes if required.
- Coat the board (solder resist) except where soldering will be required.
- Silk screen print component legends.
-
Printer, Inkjet - Computer printer that prints Bit
Images by scanning sequentially over the paper or
film and squirting
ink, hot wax, or whatever, onto it.
These printers are generally very cheap and surprisingly accurate. Colour inks can produce very high quality reproduction, but most have very poor stability - a few weeks in daylight (or a day in direct sun) will substantially change the colour rendering. -
Printer, Laser - Computer printer that prints Bit
Images using an electrostatic technique to deposit
'toner' (a magnetic
pigment powder) on the paper or film, which is then
fused with the base material using heated rollers.
These printers are generally very cheap and surprisingly accurate, or at least reproducible (i.e. can be accurate once calibrated). The toner materials are generally fairly stable. -
Printer, Electrostatic - A device similar in concept to a Laser Printer but usually capable of printing onto large rolls of paper or film.
-
Project - In Vutrax, a complete set of Schematics, layouts, Design Rules, Job Library, PCB layout, Photoplot and CNC data, Parts lists etc. for a single job
-
PTH - See Plated Through Hole
R
- Two or more signals having a critical timing relationship (e.g. a changing data signal and a clock edge used to sample it) that are poorly designed so that it depends which 'wins the race' to arrive first. Track length may be a critical issue in avoiding these problems on critical signals.
-
Radius - As a verb - To apply a Fillet.
-
RAM Routing - See Bus Routing
-
Raster Image - See Bit Image
-
Rats Nest - The interconnections of a PCB before they are assigned to appropriate layers and Routed to avoid one another. (Slang derived from a 'tangled mess'!).
-
Rectifier - An electrical component (or in special cases a circuit configuration) that passes electrical current in one direction only. See also Diode.
-
Reconnect - In Vutrax, to insert a connection between two pins of the same signal as part of re-arranging the overall pattern for the signal.
-
Resist, Solder - See Solder Resist.
-
Resistance, Track - The DC Resistance of a length of PCB track. Typical measurements are between two pins, the overall length, or the worst case in a 'star' Network.
-
Resistivity - Resistivity uses Greek letter Rho where
- Resistance = Rho * length / cross sectional area
- Rho (Ohm Metres) = Resistance of 1 metre length of material with 1 square metre cross section.
- Rho (Ohm Metres) = Rho (Micro-Ohm metres) * 0.000001(E-6)
- Rho (Ohm Metres) = Rho (Ohm cm) * 0.01(E-2)
- Rho (Ohm Metres) = Rho (Micro-Ohm cm) * 0.00000001(E-8)
The default value is that for pure copper at 20 degrees C is 1.68E-8 (0.0000000168) Ohm Metres
-
Resistor - A component that nominally 'resists' electrical current flow in a linear manner - i.e. doubling the voltage applied doubles the current. The values of the component is specified in Ohms. See Ohms Law.
-
Renumber, Hierarchy - In Vutrax, assigning silk screen legends in some logical sequence based on the layout of a series of Schematic drawings organised into a hierarchy.
-
Renumber, PCB - In Vutrax, assigning silk screen legends in some logical sequence based on the layout of the PCB.
-
Renumber, Schematic - In Vutrax, assigning silk screen legends in some logical sequence based on the layout of the Schematic drawing.
-
RF - Radio Frequency - High frequencies typically associated with radio communications (104 to 1012 Hz).
-
Rip-up Autorouting - See Automatic Routing.
-
Routing - The process of converting a Rats
Nest to a viable connection pattern without crossing
tracks, going
outside the board area, entering disallowed areas, etc.
This can be accomplished manually - i.e. by explicitly arranging signals interactively, or by using Automatic Routing.
Many complex layouts require a combination of both automation and the skill of the layout specialist to achieve economic solutions. -
RS-274D - The basic specification of data for Gerber Photoplot output. Generally consists of drawn lines, curves and flashes of 'apertures' - selectable shapes for pads or for drawing lines.
-
RS-274X - Extended form of RS-274D used to provide data for Gerber Photoplot. The primary advantage over the older standard is that apertures can be defined without the file (making it self contained) and various bit map based functions are available.
S
- A symbolic drawing. In the electronic sense consists of a series of symbols for electronic components with lines or explanatory labels indicating how they are interconnected. Often include indication of the identifying legends used on the PCB and pin numbers, but none of the physical layout.
-
Schematic Capture - Analysing a computer drawn Schematic to determine the interconnections it represents. In Vutrax this generates a Device Oriented List which is merged automatically with others in a hierarchy of drawings to be processed into the Rats Nest.
-
Schematic Library - See Libraries.
-
Screening - Providing an earthed, conducting box, outer sheath, or area of copper on a PCB to protect whatever is within from external electrical interference, or from generating such interference.
-
SCSI - Small Computer System Interface - a parallel interface standard widely used for interfacing high performance disk drives, scanners, printers and similar peripherals. Exists in both internal and external forms. There have been many revisions of bus width and speed (including new external connectors for each) but even so manages a surprising success at compatibility..
-
Segment - In Vutrax, any straight line or track between two 'points'.
-
Shape Based Autorouting - See Automatic Routing and Specctra.
-
Silk Screen - Printing on the component side (sometimes both sides) of a PCB that uses outlines and symbols to show component locations, and identifies particular components with Legends.
-
Signal - A Digital or Analogue voltage or current that passes
between components.
More casually, the pieces of track that join together 2 or more pins. -
Simulation - Determining the (likely) behaviour of a circuit by using numerical techniques to calculate the effects.
-
Simulation, Analogue - Determining the (likely) behaviour of a circuit by examining voltage and current levels (time domain) or frequencies (frequency domain), using models of components to determine behaviour by using numerical techniques to calculate the effects.
-
Simulation, Logic - Determining the (likely) behaviour of a logic circuit. Generally exact voltage levels and frequencies are ignored - the simulation is used to determine that the logic performs the appropriate operations.
-
Simulation, Mixed - A combination of various types of simulation to produce a more general simulation at the cost of time and complexity.
-
Single in Line - A component with all its pins in a single row, often at 100 THOU or 50 THOU pitch.
-
Single Sided - A circuit board with tracks on one side only. Most
practical designs of this type include many Wire
Links".
See also Double Sided and Multilayer. -
SMD - See Surface Mount Device.
-
SMSO - Surface Mount Small Outline - a standardised footprint.
-
SMSOL - Surface Mount Small Outline - a standardised footprint with wider row separation that SMSO.
-
SMLCC - See Surface Mount and Leadless Chip Carrier.
-
Solder Cream - See Solder Paste
-
Solder Mask - See Solder Resist
-
Solder Paste - One technique for soldering Surface
Mount components is to place solder paste on the
pad, and
then melt these en-masse using infra-red heaters or hot
gas..
See also Solder Wave. -
Solder Resist - A coating that during manufacturing prevents solder wetting undesirable areas, and on the finished PCB protects traces from physical damage, chemical attack, and to help minimise or control stray capacitance. Usually applied by silk screen printing (less often by lamination) to the whole surface of both sides of the board not requiring soldering or contact for heat sinks. Usually green in colour, but may be clear or other colours. Small scale production may obtain to same protection using a conformal coating. Also known as Solder Mask
-
Solder Wave - One technique for soldering Surface
Mount and the primary technique for conventional
components,
is to arrange that a 'wave' of molten solder ripples
along back side of the board.
See also Solder Paste. -
Soldering SM - Soldering Surface Mount is usually accomplished using one of Solder Paste or Solder Wave. See also Glue Spot.
-
Spanning Tree Optimisation - Interconnecting a series of points (component pins) using the minimum total length. For PCB purposes the total length may be measured as right angle length rather than point to point, to reflect the natural layout of most Routed boards.
-
Specctra - Trade name for Shape Based Autorouting software. See Automatic Routing.
-
SRBP - Synthetic Resin Bonded Paper - a material widely used as a Substrate for low cost single or double sided boards, such as non-critical parts of TV Sets. American name is CEM1.
-
Spiral - A Curve that decreases in radius linearly with angular radius. Primary use in electronic design is to create an Inductor.
-
Step - In Vutrax, the coordinate distance travelled for each press of an arrow key, or the 'snap' of the Cursor when the mouse is moved.
-
Step and Repeat - An operation that performs some function and then moves down a fixed amount. e.g. Placing rows of component pins, Duplicating a whole PCB layout to Panellise a design.
-
Stripline - A technique to tightly control the Transmission Line characteristics of a PCB trace by running parallel tracks for signal and return path, or differential pair.
-
Substrate - The base material of a PCB onto
which the Copper tracks and subsequent
coating (e.g. Solder
Resist) are applied.
Examples of these materials are Fibreglass, SRBP, FR4, CEM1, Polyimide, Duroid and Teflon.
Specialist ceramic materials are often used for Hybrids. -
Surface Mount - A style of component mounting where the component
'pins' are soldered to Pads on either
side of the
PCB, with no hole required through the
pad.
See also Glue Spot, Solder Wave and Solder Paste. -
Susceptibility - Causing malfunction of a circuit by electromagnetic interference from external sources. See EMC.
-
Swop, Gate - See Gate Swapping.
-
Swop, Group - See Group Swapping.
-
Swop, Pin - See Pin Swapping.
T
- The point (in Schematic or a PCB Layout) where a connection is made to another by contacting it at some position along a line (as in the upright of a letter T contacting the top bar). In Schematic diagrams the join is often emphasised with a blob (Vutrax Node) to match the marker necessary when crossing line are interpreted as connected (better turned into two T-Junctions).
-
Teardrop Pad Shape - A basically circular Pad with one side stretched out to provide a connection point.
-
Technical Drawing - Mechanical line drawings produced in a variety of Projections. See 3rd Angle projection and Isometric Projection.
-
Technical Support - Somebody to Phone or e-mail when something has gone
wrong, or you can't see how to do what you
need. Even better if the contact knows enough about the
product and the business to help you.
The Vutrax Technical Support address is support@vutrax.co.uk or Telephone +44 (0)1525 261 381 -
Teflon - A material used as a Substrate for a PCB. Used in high frequency designs where its great stability outweighs its expense and hazardous manufacturing process.
-
Test Point - An exposed metal area of the board (usually a pad of bare copper area on a PCB) that provides contact for a Bed of Nails tester or an engineers test probe.
-
Thermal Analysis - Estimating the thermal (temperature) performance of a design to determine whether changing layout would reduce 'hot-spots'. e.g. Adding Heat Dissipators (Heat 'sinks' or exposed areas of tracks), spreading out components with high dissipation, aligning components with the air flow.
-
Thermal Break - Used for improving soldering of holes connected to a powerplane. See Broken Ring.
-
Thermal Characteristics - How a component's behaviour changes with temperature. Quite extreme ranges often have to be considered for component that substantially self heat. Some devices, such as Thermistors, are often used for their thermal characteristics rather than these being a nuisance.
-
Thermal Cutout - See Thermal Break
-
Top Down Modification - See Forward Modification.
-
Token Ring - A LAN technology based on a ring of computers passing a token around the loop.
-
Trace - See Track.
-
Trace Pad - In Vutrax, the style of the available Pad Shapes where the user defines the detailed outline.
-
Track - A copper 'line' on a PCB to conduct signal current.
-
Track Between Pins - A level of PCB technology that permits
signal tracks to pass between typically spaced component
Pads pads.
For conventional 0.1" pitch, 0.064" diameter pads, 0.012" tracks and 0.012" minimum gap is considered easy.
For Surface Mount with 0.05" pitch devices requires much more tight control. Very high level design may use tracks and clearance of 0.003" with multiple tracks between pins. -
Track Clearance - The minimum permitted close approach to another signal. Some signals (e.g. high voltage) may have a limit set by electrical or safety consideration rather than accuracy of board manufacture.
-
Track Impedance - The effective impedance of a track as determined by its width and association with other tracks and any groundplane. See also Stripline.
-
Track Necking - Narrowing of a PCB track to fit through a small space, for example to go between component pins. Wide tracks have advantages in being less likely to be manufactured with discontinuities, less likely to crack over time, carry current with less heating, and therefore less stress on adhesives. Thus it is common to narrow a track only where necessary. See Track Width.
-
Track Routing - Arranging the connections in a Rats Nest to achieve the required interconnections with no shorts or inadequate clearances. See Routing.
-
Track Width - The width of a Track on a PCB is determined by a combination of
factors:-
- Must be wide enough that manufacturing is able to reliably produce a track with no breaks.
- Must be narrow enough to accommodate the density of signals required on the design.
- Must be wide enough to carry the necessary current without excessive heating - see Track Current Capacity.
-
Track Shuffling - Mass moving a selection of Tracks, usually to pack them with minimum clearance to make room for further connections through the same area of the PCB.
-
Track Pattern - Often groups of Tracks are routed in a similar pattern. Vutrax offers a feature to automate this process. See also Bus Routing
-
Track Current Capacity - This is a quite complex area - there is a treatise on it at the Vutrax web site. See also Track Width.
-
Transistor, Bipolar - A transistor where the current between Emitter and Collector is determined by a smaller current applied to the Base (i.e. a current amplifier).
-
Transistor, FET - A Field Effect Transistor - the current between Source and Drain is determined by the electrical field from an isolated Gate (i.e. voltage control).
-
Transmission Line - On PCBs, a term referring to designing track layout to
have an accurately defined Track
Impedance,
often consisting of a pair of conductors (either
differential or signal and return) running in parallel.
See also Stripline and Microstrip -
TTL - Transistor Transistor Logic was the initial implementation of the 74xxnnn series logic (TTL being the form with xx omitted).
U
- An operating system dating back to 1970 still widely
used for Networks of various sorts
(most
Internet infrastructure machines use
some form of UNIX) and increasingly as a personal
operating
system. It is designed to be secure and extremely
reliable - systems can run continuously for years.
Available for a wide variety of processors, but limited in acceptability until recently because of lack of cooperation between competing development companies
A graphical front-end X-Windows is available.
See also Linux. -
URL - Uniform Resource Locator - the textual form of
addresses on the Internet. Note that separators are
always '/' rather than '\'. e.g. the Vutrax web
site has the URL
http://www.vutrax.co.uk/index.htm Protocol: xxxx Internet Site: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx File name (can include directories): xxxxxxxxx
V
- An image stored as a series of drawn lines. As such
they can be scaled up and down without
distortion, and easily manipulated to alter positions of
items.
Modern display technology displays images using Bit Image techniques. Conversion of a Vector image to a Bit Image at a chosen scale is easy. Once in this form conversion back to a vector image, or changing of scale, is a slow and unpredictable process.
Examples of Vector Images are Vutrax and AutoCAD DXF graphics formats. -
VIA - A hole drilled through the board that is then plated,
to provide selected connections between traces
and/or Groundplane on different
layers (or on Double Sided board,
just the two sides).
Some low cost or ad-hoc manufacturing processes do not provide the plated-through hole (which is difficult to manage without use of horrid chemicals and complex processing) and instead 'pin through' necessary connection, or arrange for layer changes to occur at components that can be soldered on both sides.
See also Laser VIA, Buried VIA and Blind VIA. -
VIA, Laser - A VIA produced by laser burning/evaporating holes. Such VIAs can be very small, and Blind VIAs can be produced in the same pass as through board VIAs by providing reflective copper at the 'deepest' layer.
-
VIA, Blind - A VIA that appear on one surface of a
multilayer PCB, but stops part way through. PCBs may use
a
variety of Blind and Buried styles
to attain higher densities.
See also Laser VIA. -
VIA, Buried - A VIA connecting inner layers of a
multilayer PCB, but does not appear at either surface.
PCBs may
use a variety of Buried and Blind
styles to attain higher densities.
See also Laser VIA. -
Void - In Vutrax, the name assigned to a rectangular 'Keep out' area used during Automatic Placement or Automatic Routing
-
Vutrax - A PCB design system designed for
professional users, including an integrated system for Schematic
entry through to finished PCB, including automated
updating when revisions are applied to either the
Schematic (Forward
Modification") or to the PCB (Backward Modification").
The Vutrax web site is at http://www.vutrax.co.uk
W
- WAN
- Wide Area Network - a geographically separate network using interconnection technologies such as land-lines and Modems.
- A set of (nominally) HTML pages and
associated images, sound and executable files, linked to
form
a resource for access over the Internet using a Browser
See also URL.
The Vutrax web site is at http://www.vutrax.co.uk -
Windows - Tradename of Microsoft Corp, and the general name of their range of Graphical User Interface operating systems.
-
Windows GDI - See GDI
-
Windows 95 - Microsoft Windows operating system
launched in 1995. Although based on a 16 bit GDI it is
designed to support 32 bit applications.
Windows 95 was actively developed for 4 years and systems vary substantially according to revision. -
Windows 98 - A development of Windows 95
-
Windows ME - A development of Windows 98 that introduces some self repair, but removes direct port access.
-
Windows NT - Microsoft Windows operating system based on a full 32 bit GDI and applications interface. It includes high levels of security and protection of the operating systems from application errors. Supports most 16 bit applications, but many DOS application requiring direct access to the hardware will not work.
-
Windows NT 3.51 - First widely used version of Windows NT
-
Windows NT 4.00 - Widely used version of Windows NT
-
Windows XP - A Merging of Windows 2000 and Windows ME into a unified platform.
-
Windows 2000 - Development of Windows NT incorporating much of the look and feel of Windows 98
-
Wirewrap - A form of prototyping, small quantity, or customised
wiring. Insulated wires with about 1" stripped at
each end are wrapped around square posts using a
special tool to ensure that gas-tight connections
are formed at the corners of the post.
Remarkably untidy and bulky, but also reliable (if kept clean) and (relatively) easy to modify. Vutrax supports output of tables for systematic wrapping of connections (including wire length) and tables for checking more optimally than with the primary list. -
Wire Link - Simply, a connection accomplished by using a wire
connecting parts of the board. These may appear
on any complexity of design where routing is impossible,
uneconomic, or as a result of modifications.
More specifically, on Single Sided designs, many automatically inserted bare wire links may be used to make complete connections not possible without a second orthogonal layer.
Slang form: Zero Ohms Resistors.
X
- A graphical front end (presentation layer) primarily
used for UNIX systems, although
implementations
are available for DOS and Windows.
Various windows managers provide various options for look and feel.
© 2003 Computamation Systems Ltd.